【位运算】801. 二进制中1的个数
使用 lowbit 查找出二进制中 1 1 1
1 2 3 int lowbit (int x) return x & -x; }
每次进行 lowbit ,然后减去 lowbit(x) 直到为 0 0 0
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 );cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); int n; cin>>n; while (n--){ int k,a = 0 ; cin>>k; while (k > 0 ) k -= (k&-k),a++; cout<<a<<" " ; } }
三分
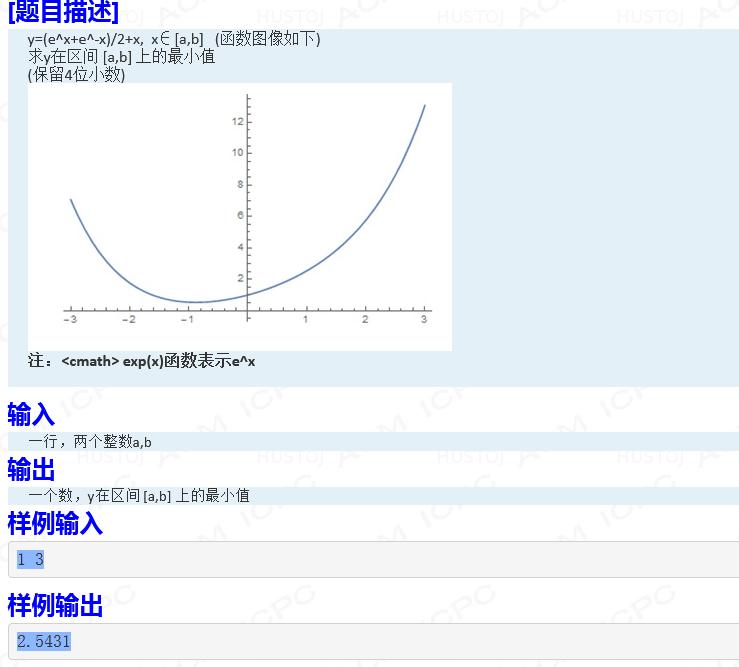
点击展开题面
直接套三分模版。l m i d , r m i d lmid,rmid l m i d , r m i d
1 2 double lm = l + (r - l) / 3.0 ;double rm = r - (r - l) / 3.0 ;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const double eps = 1e-5 ;double f (double x) return (exp (x) + exp (-x)) / 2 + x; } int main () double l, r; cin >> l >> r; while (abs (l - r) > eps) { double lm = l + (r - l) / 3.0 ; double rm = r - (r - l) / 3.0 ; if (f (lm) > f (rm)) { l = lm; } else { r = rm; } } cout << fixed << setprecision (4 ) << f (l); }
哈希
朴素哈希(unordered_map)
【哈希表】840. 模拟散列表
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const double eps = 1e-5 ;unordered_map <int ,int > mp; int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 );cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); int q; char op; int x; cin>>q; while (q--){ cin>>op>>x; if (op == 'I' ){ mp[x]++; }else cout<<((mp[x] == 0 ) ? "No" : "Yes" )<<"\n" ; } }
字符串哈希
之前的博客有讲过。
这次注意的点:在求 c h a r char c h a r 1 1 1 strlen(char+1) 而不是唐氏的 strlen(char)-1。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int P = 131 ;char s[1000100 ];unsigned long long h[1010100 ], p[1010000 ];void gethash () int len = strlen (s+1 ); p[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= len; i++) { p[i] = p[i - 1 ] * P; h[i] = h[i - 1 ] * P + s[i]; } } unsigned long long get11 (int l, int r) return h[r] - h[l - 1 ] * p[r - l + 1 ]; } int main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cout.tie (0 ); int n, q; cin >> n >> q>> (s + 1 ); gethash (); for (int i = 1 ;i <= q;i++){ int a,b,c,d; cin>>a>>b>>c>>d; if (get11 (a,b) == get11 (c,d)){ cout<<"Yes\n" ; }else { cout<<"No\n" ; } } }
二分
数的三次方根
tips: 这里不放标准解法了,水一发立方根函数 double cbrt(double x)。直接求 x 的三次方根。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;int main () double x; cin>>x; cout<<fixed<<setprecision (4 )<<cbrt (x); }
P2678 [NOIP 2015 提高组] 跳石头
题解见Here ,这个写的很有实力
Warning:如果你过不了样例,可能是你二分的 l l l l l l
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 2e5 +10 ;#define int long long int n, m, d;int a[50010 ];bool check (int mid) int tot = 0 ,i = 0 ,now = 0 ; while (i < n+1 ){ i++; if (a[i]-a[now] < mid) tot++; else now = i; } return tot <= m; } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); cout.tie (0 ); cin >> d >> n >> m; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } a[n+1 ] = d; int l = 1 , r = d,ans = 0 ; while (l <= r) { int mid = l + r >> 1 ; if (check (mid)) l = mid + 1 ,ans = mid; else r = mid - 1 ; } cout<<ans; }
离散化
【离散化】802. 区间和
一开始打桶排序前缀和的时候循环范围没设置好导致发生了一些TLE的莫名错误
然后吸氧+关同步流过了一半,WA。
然后数组开小了。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 #pragma GCC optimize(3) #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 2e5 +10 ;#define int long long int c[N], a[N], b1[N], b2[N], d[2 *N];int ton[5 * N];int k, n, q;vector<int > v; signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 );cin.tie (0 );cout.tie (0 ); cin >> n >> q; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i] >> c[i]; v.push_back (a[i]); } for (int i = 1 ; i <= q; i++) { cin >> b1[i] >> b2[i]; v.push_back (b1[i]); v.push_back (b2[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < v.size (); i++) { d[i+1 ] = v[i]; } sort (d + 1 , d + 1 + v.size ()); k = unique (d + 1 , d + 1 + v.size ()) - d - 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) { a[i] = lower_bound (d + 1 , d + 1 + k, a[i]) - d; ton[a[i]] += c[i]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= k; i++) { ton[i] += ton[i - 1 ]; } for (int i = 1 ; i <= q; i++) { b1[i] = lower_bound (d + 1 , d + 1 + k, b1[i]) - d; b2[i] = lower_bound (d + 1 , d + 1 + k, b2[i]) - d; cout<<ton[b2[i]]-ton[b1[i]-1 ]<<"\n" ; } }